- Research and development
- Philosophy
- History
- Contacts
- Locations
- Country representatives
- Risers
- NET-Technology®
- Special molding materials

Support consultants
Support consultantsProfessional Applications Engineers
Individual customer solutions
Individual customer solutionsFlexible production – for one unit or more
GTP Schäfer ToolBox
GTP Schäfer ToolBoxFoundry 4.0
Simulations
SimulationsData on materials and geometry available in MAGMA

Company Policy
Company PolicyThe principles of our daily actions
Corporate Responsibility
Corporate ResponsibilityAs a company with a focus on sustainability, we are happy to share our success with others and support local and international projects.
THERMO-Riser®
THERMO-Riser®Feeding systems with a high level of individualisation
Exothermic / insulating caps
Exothermic / insulating capsExothermic and insulating caps for ramming up and insertion
PXT-PKXT-Riser
PXT-PKXT-RiserHighly exothermic riser sleeves, specially designed for use on high-pressure moulding lines
POINT-Riser®
POINT-Riser®Highly exothermic riser sleeve especially for use on moulding plants
ECO-Riser®
ECO-Riser®Solving challenges in the smallest of spaces
FILTER-Riser
FILTER-RiserIncreased outputs due to reduced circulation
FIBRE-Sleeves
FIBRE-SleevesConventional riser system with intelligent accessories for large castings
ISO-Riser
ISO-RiserCost reductions by using POINT-accurate risers made of non-ferrous metals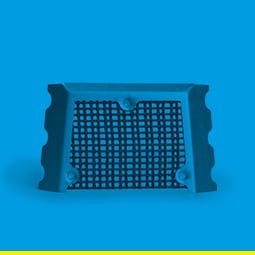
NETFrame®
NETFrame®Easy riser removal and improved process efficiency
NETCore®
NETCore®Breaking Edge “0”
NETSleeve®
NETSleeve®Maximum feeder performance for largest possible module
